 While there are many risks inherent in international trade finance, there are also numerous solutions available to exporters and importers to manage and mitigate risks. In most developed countries, an organization can draw on a wealth of free or inexpensive expert opinions to assist with risk mitigation for financial transactions.
While there are many risks inherent in international trade finance, there are also numerous solutions available to exporters and importers to manage and mitigate risks. In most developed countries, an organization can draw on a wealth of free or inexpensive expert opinions to assist with risk mitigation for financial transactions.
Major banks, such as Royal Bank of Canada, Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, BNP Paribas and HSBC, have large portfolios of international loan assets and maintain extensive international financial networks. To safeguard their interests and those of their customers, banks employ large staff of political analysts and international economists, and are often willing to share their expert opinions and written reports.
Embassies and consulates abroad, as well as commercial officers, are valuable sources of political, economic and commercial risk information. These resources can often provide information on a target country’s current business environment, as well as credit and business information about potential customers.
Solutions available to mitigate some of the most common commercial risks to ensure successful international transactions include those represented in the figure below.
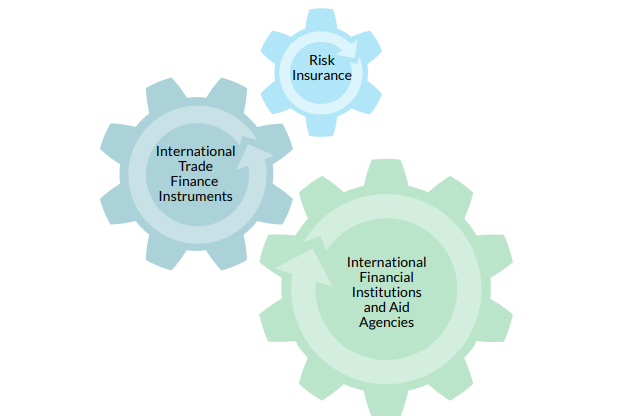
These options are explored in the following sections with guidelines for both the importer and exporter.
Want to learn more about payment, risk mitigation, financing, and the flow of goods and services. Check out the International Trade Finance FITTskills online course.
1. International Trade Finance Instruments
Trade finance instruments have evolved slowly since their introduction to the market, some as early as several hundred years ago. They have been gradually adapted to the changing needs of organizations trading internationally. In more recent years, several factors have contributed to a heightened need for traditional banking instruments to adapt while still providing commercial parties with protection, security and risk mitigation. These factors include:
- Rapidly changing role of technology
- Electronic transmission of shipping and title documents
- Acceptance of electronic transfer of title
- Large-scale movement toward trade on open account.
An organization should select the financial instruments that best address its needs and identified risks, as well as those that respond to the underlying dynamics of a commercial contract. In general, importers and exporters must agree on terms and methods of payment based, in part, on the risks associated with planned transactions.
In low-risk transactions, such as those between parties with established and trusted commercial relationships, organizations often use documentary collections. Open account terms are similarly well suited for established relationships, although companies that use these instruments must pay more attention to risk mitigation now than in the past. Documentary letters of credit offer protection to both importers and exporters. Confirmed letters of credit give exporters even more protection and, as such, are used effectively in the most high-risk markets in the world.
2. Risk Insurance
Businesses that engage in international trade can mitigate commercial risk and protect its interests through various forms of insurance, including:
- Cargo insurance
- Political risk insurance
- Foreign accounts receivable insurance
Indeed, insurance options are available to address nearly every category of risk that suppliers and buyers could possibly encounter while conducting international commerce.
Political risk insurance (PRI) and accounts receivable insurance (ACI) are particularly common, and can be obtained from specialist private sector providers or, depending on the market, from public and private entities such as export credit agencies (ECAs).
Established in post-war Europe as part of a broad reconstruction strategy, ECAs were originally public sector entities that promoted exports by providing various financing and risk mitigation products and solutions.
In recent years, however, many of these organizations have been fully or partially privatized and now have mandates that extend beyond their original public sector focus. In fact, just before the onset of the recent global financial crisis, many questioned the need for ECAs in international trade.
However, their critical value was demonstrated when the market collapsed and private sector providers retreated in panic. Variations on the ECA model continue to be numerous, with the approach and the scope of ECA-like organizations varying almost by country. Many ECAs now offer political risk insurance and foreign accounts receivable insurance, which are both important forms of coverage that can help exporters offset trade-related commercial risks. Unit 3 provides further details on how organizations can use ECAs to mitigate commercial risk.
3. International Financial Institutions and Aid Agencies
International financial institutions (IFIs), such as the World Bank’s International Finance Corporation, and regional development banks offer financing and risk mitigation programs that facilitate the conduct of international trade by engaging local banks in international trade finance and enhancing trade flows.
Some examples of such regional development banks include:
- Asian Development Bank
- European Bank for Reconstruction and Development
- Inter-American Development Bank
- International Islamic Trade Finance Corporation
Several IFIs have developed programs specifically to address the risk profile of their local banks, providing guarantees so international banks are more likely to extend confirmations to the documentary letters of credit issued by local banks. Without these guarantees, the risk profile of IFI-affiliated local banks would be such that international banks would either refuse requested confirmations outright, or charge high fees for them.
Many international aid agencies and development finance institutions also provide financing or risk mitigation solutions. These solutions foster increased trade flows with higher-risk developing and emerging markets, which helps encourage development and reduce poverty in these markets.





disqus comments